TLC or Thin Layer Chromatography is a simple and popular chromatographic technique used to extract and analyze various non-volatile individual components from mixtures. This technique is generally conducted on a plastic sheet or glass plate after finely splitting it with various adsorbent materials like cellulose, silica gel, or Aluminum oxide. These adsorbents have the characteristics to attract and retain various components from the mixtures.
A small amount of sample mixture is spotted onto the one end surface of the TLC plate (stationary phase) and placed vertically into a closed chamber with a suitable organic solvent which acts as the mobile phase. The solvent is then traveled up the TLC plate by capillary action. The components from the mixture migrate different distances based on their differential interactions with the adsorbent differently.
The Thin Layer Chromatography plate should be removed from the developing chamber for drying when the mobile phase solvent reaches the top of the plate. The separated components appear on the Thin Layer Chromatography plate as discrete spots. Then the retention factor (Rf) can be evaluated easily after identifying the spots because each spot contains a retention factor (Rf) which is expressed as the following:
Retention factor (Rf) = dist. traveled by extract sample / dist. traveled by solvent
The various factors such as solvent characteristics, types of adsorbent, amount of material spotted, and temperature create various effects during analysis by this technique.
Principle of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
TLC technique is used in various fields of chemistry for separating various components from the mixtures. The separation depends on the relative attraction of components toward both phases. The solvent from the mobile phase moves over the surface of the stationary phase where the sample mixture is placed. The movement of the solvent occurs in a way that the components which have a strong affinity to the stationary phase move slowly while the other compounds travel very quickly from the sample mixture.
Then the separation of components can be occurred as various spots after traveling the mobile phase through the mixture of the components on the stationary phase sheet. The individual component is then identified by various detection techniques based on their character and nature. Thus we can determine the composition of the sample mixtures easily by TLC chromatography technique.
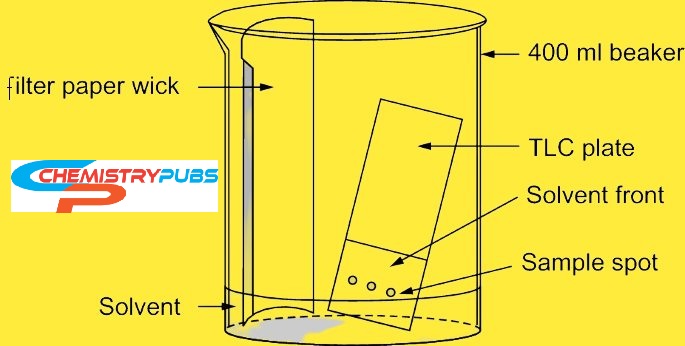
Components of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
Thin Layer Chromatography system consists of the following parts:
TLC plate: This plate is made of glass sheet or plastic material which acts as a stationary phase. TLC plate should be stable and chemically inert. This plate has uniform thickness and is in fine particle size for showing good activities.
TLC chamber: This chamber maintains a good uniform environment inside the TLC plate for the development of spots. It helps to prevent any kind of dust as well as the evaporation of organic solvents.
Mobile phase: this phase is made by a solvent or solvent mixture. This phase should be free from any particulate as well as give the highest purity for proper development of TLC spots. The solvent of the mobile phase should be chemically inert with the sample, a stationary phase.
Filter paper: This paper is placed inside the chamber to moisten the mobile phase. This paper is very important to get a uniform rise in a mobile phase over the length of the stationary phase.
Experiment Procedure of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
At first, the material of the stationary phase should be applied to the plate which must make it dry and stabilize. The sample mixture can be placed at the bottom of the plate after marking with the help of a pencil. The solvent of the mobile phase is then placed in the TLC chamber and closed it with something. It should be kept in such a way that the sample can face the mobile phase easily.
It can immerse the TLC plate for a definite period of time for proper development. It must be remembered that the sample mixture spots must be above the solvent. The component spots from the mixture can be found after proper interaction with the mobile phase and stationary phase. Then the TLC plate should be removed and dried properly which can be observed under a UV light chamber.
Applications of thin-layer chromatography
This chromatography technique is used for monitoring the reaction rate. It can be possible to identify various compounds present in a sample mixture. The purity of various substances can be detected by this technique. The various harmful pesticides or insecticides in food and water can be identified with the help of this process. The dye composition of fibers in forensics is justified easily by this easy technique. The medical plant’s compositions can be analyzed by the TLC process.
Advantages of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
TLC technique is a modern versatile technique which can be done with a short development time. The isolated components can be separated easily. This chromatographic technique is the cheapest and easiest technique for separating various components from the sample easily.
Disadvantages of Thin Layer Chromatography
The stationary phase in the TLC process does not have longer stability. It is very difficult to reproduce the results generated from the TLC technique. Various factors such as humidity and temperature can affect the final outcome of the results. This technique can not be effective for quantitative analyses.
References
1.Bele, A. A., & Khale, A. (2011). An overview on thin layer chromatography. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 2(2), 256.
2.Sherma, J., & Fried, B. (Eds.). (2003). Handbook of thin-layer chromatography. CRC press.

