A buffer solution is a one-type aqueous solution that has the ability to resist the change in its pH value after adding a small amount of strong acid or base. This solution consists of a mixture containing a weak base and the conjugate acid of the weak base (basic buffer) or weak acid and the conjugate base of the weak acid (acidic buffer).
We know, the pH value of the acidic solution is below 7 and the pH value of the basic solution is above 7. This solution has an acceptable amount of a weak conjugate acid-base pair. The characterization of this solution is determined by the added amount of the weak conjugate acid-base pair before the pH begins to change significantly.
It maintains the specific pH level and neutralizes the added acid or base effectively to keep a constant pH level of solutions. There are many buffer solutions that are added into solutions to remove the wrong outcome to conduct the experiment smoothly.
Buffer Solution Definition
A solution containing definite amounts of a weak conjugate acid-base pair to control the value of pH in solution significantly is known as a buffer solution. The addition of a small amount of acid or base is unable to change the value of pH in this solution. This solution controls the hydrogen ion concentration to keep the constant pH value of the experiment solution strong.
This solution is essential in the field of acid-base chemistry. This solution helps to neutralize some of the added acid or base so that the pH cannot change more gradually. This can be done by reacting hydrogen ions with hydroxide ions so that they cannot affect pH at maximum capacity. A lot of experiments and analyses with strong acids and bases become easier by using this solution.
Buffer Solution Examples
A solution is prepared by mixing a specific amount of acetic acid (weak acid) and sodium acetate (salt) (CH3COOH + CH3COONa).
A solution is prepared by mixing a specific amount of ammonia (a weak base) and ammonium chloride (salt) (NH3(aq) + NH4Cl(aq)) which controls the pH value effectively.
A solution of Formic acid & conjugate base: HCHO2 & CHO2–
A solution of Pyridine & conjugate acid: C5H5N & C5H5H+
A solution of Methylamine & conjugate acid: CH3NH2 & CH3NH3+
Types of Buffer Solutions
There are two types of these solutions namely acidic and alkaline buffers.
Acidic Buffers
Acidic buffers are used for controlling acidic environments. The pH value of the acidic buffer is below 7. Acidic-type buffer is prepared by mixing a weak acid and its salt with a strong base.
Acidic Buffer Examples
A solution containing the mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate in water (CH3COOH + CH3COONa) and a solution of formic acid and sodium formate in water (HCOOH + HCOONa) are examples of acidic buffers. The acidic buffer from the mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate has a pH of 4.74.
Alkaline Buffers/Basic Buffers
Alkaline buffers are used for experimental purposes or processes for controlling the basic environment. This alkaline buffer is generally prepared by the addition of a weak base and its salt with strong acid. The pH values of alkaline buffers are more than 7.
Alkaline Buffer/Basic Buffer Examples
A solution containing a mixture of ammonium hydroxide and ammonium chloride in water (NH4OH + NH4CI) and a mixture of ammonium hydroxide and ammonium nitrate in water (NH4OH + NH4NO3) are examples of alkaline buffer solutions. Alkaline buffer from the mixture of ammonium hydroxide and ammonium chloride has a pH of 9.24.
Buffer Solutions Mechanisms
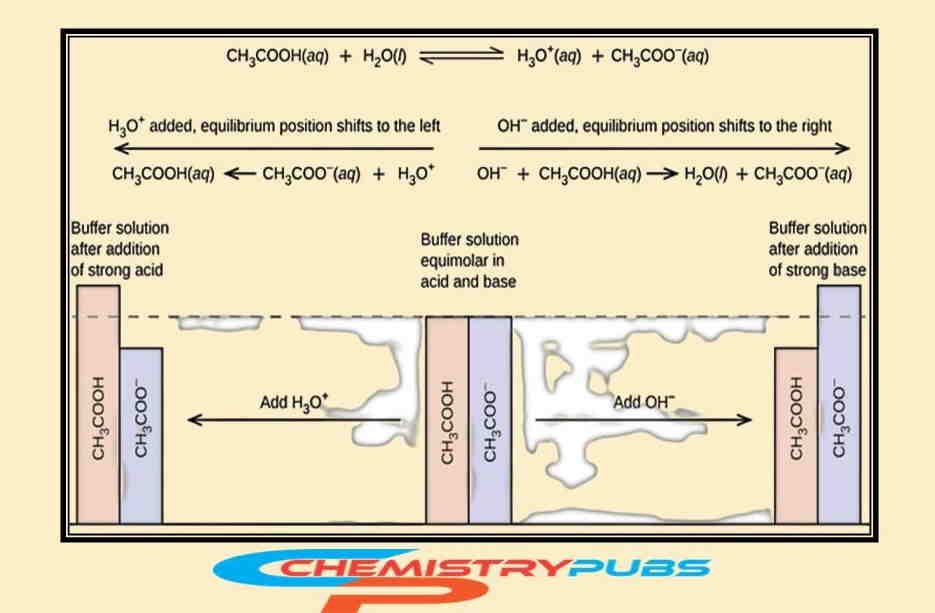
To understand the mechanism of this solution, one can consider a buffer solution prepared with equal amounts of acetic acid and sodium acetate. The addition of a modest amount of acid and base into this solution cannot change the pH of the buffer solution.
To illustrate this phenomenon, it is noted that the hydronium ions are neutralized and shift the condition of acetic acid ionization equilibrium to the right after adding a strong base into this solution. Likewise, the acetate ions are neutralized and shift the ionization equilibrium conditions to the right position returning the hydronium ion [H3O+] to near its original value.
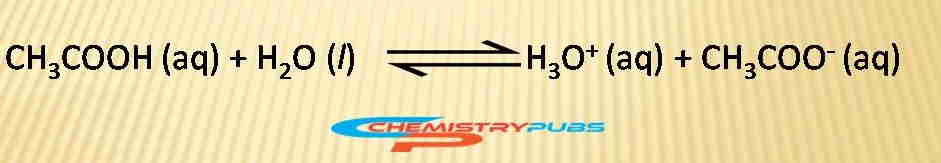
An image is given below to understand clearly the action of this buffer solution:
Buffer Solution Preparation
There are various methods to prepare this solution with a different pH. It can be prepared by mixing an acid and its conjugate base in the first approach. Then it must dissolve the acid component of the buffer in around 60 % amount of water used to produce the final volume of this solution.
It can be used the Henderson-Hasselbach equation to determine the exact amount of acid and conjugate base required to make a buffer solution of a definite pH value.

The preparation methods of acidic and basic buffers are given below:


Importance of Buffer Solution
There is a lot of importance to using this solution which is discussed below:
This solution is very important to maintain the enzyme activity in many organisms.
The bicarbonate and carbonic acid buffer systems have great importance in regulating the pH of animal blood.
In a lot of chemical reactions pH is controlled by a buffer solution.
The buffer solution controls the pH of various biochemical reactions.
All multicellular organisms contain almost constant pH and have important effects through buffer systems.
Buffer solutions are used in pharmaceutical sectors to control the pH of various solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a buffer solution?
The solution has the ability to control the pH of its solution after adding a small amount of acid or base.
What are the types of buffer solutions?
There exist mainly two types of buffer solution namely acidic buffer solution and basic buffer solution.
What are the examples of buffer solutions?
A solution of acetic acid (weak acid) and sodium acetate (salt) (CH3COOH + CH3COONa) mixture.
A solution of a specific amount of ammonia (a weak base) and ammonium chloride (salt) (NH3(aq) + NH4Cl(aq)) mixture is an example of a buffer solution.
What is the role of buffers in pharmaceutical industries?
This solutions are used in pharmaceutical industries for controlling the pH of various solutions to prepare syrup, tablets, and a lot of medicines to regulate the pH of biological cells of organs.
What is the importance of buffer solutions?
It is very important to control the value of pH during experiments or conducting processes in industries.
What is the use of the Henderson-Hasselbach equation?
The Henderson-Hasselbach equation is very applicable to preparing the buffer solutions.

