Compound Microscope is an advanced technique used to visualize a 2D magnified image of a specimen on a glass slide. The produced image from this microscope contains high definition. This microscope has the ability to magnify higher levels of magnification if we compare it with stereo or other low-power microscopes.
This device consists of two optical parts namely the objective lens and the ocular lens. It can use two or more lenses in the objective and the eyepiece parts. The two or more double convex lenses in this microscope are fixed in a hollow cylinder.
The objective lens has a short focal length and is located at the lower part, whereas the eyepiece contains a higher focal length and is located at the upper part of this device. This microscope is heavily used in various laboratories for testing and conducting research purposes.
Two or more convex lenses in this microscope have the strong ability to magnify an image of a sample. A sample specimen is collected and put on the stage directly underneath the objective lens.
A source of light from underneath the stage illuminates the sample specimen. The image of the specimen sample appears large after spreading light on the sample. The produced image can be magnified easily by additional lenses inside the optical path length.
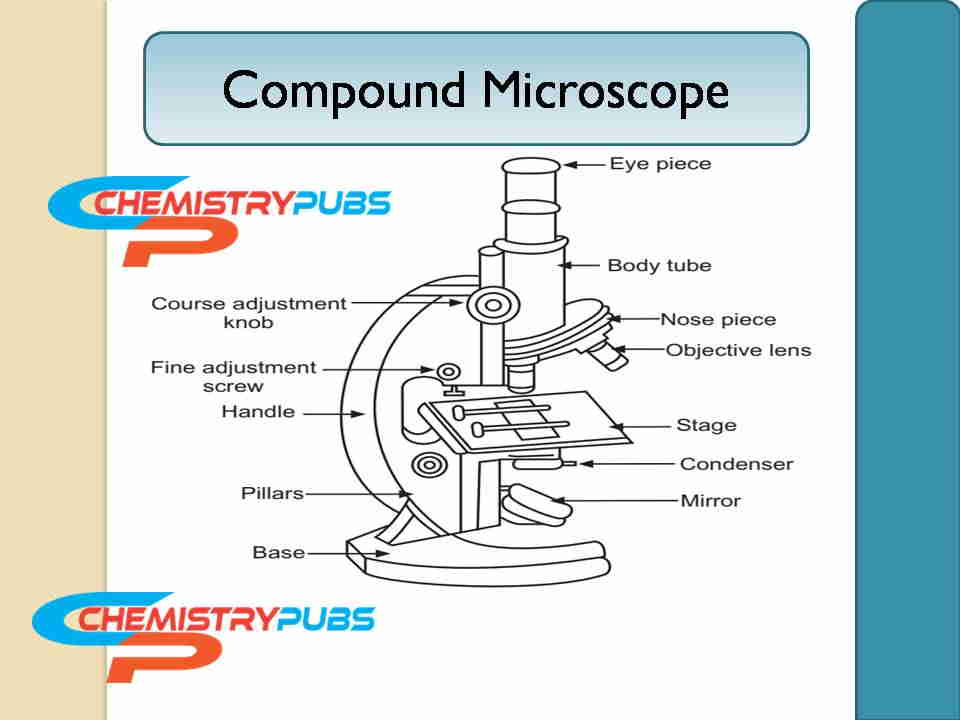
Diagram of Compound Microscope
Dutch spectacle-maker Zacharias Janssen invented this microscope in early 1590. The diagram of the compound microscope is shown below:
Principle of the Compound Microscope
This standard-type microscope consists of lenses that increase magnifying powers and the resolving power in a complex system. The sample specimen is mounted on an opaque glass plate slide and positioned on the specimen stage. The location of the specimen stage is the middle position of the condenser lens and objective lens.
A beam of incident light from the source is focused by a condenser lens onto the sample specimen or object. The light is then picked up by the objective lens transmitted by the specimen. As a result, a primary magnified image of the specimen is produced inside the body tube. The primary image is then magnified again by the eyepiece or ocular lens.
The nose piece can be rotated to bring the low-power focusing into higher power (generally 45X) in line with the help of the illuminated part of the slide if higher magnification is required. It can also be used as an oil immersion objective lens (usually 100X) to produce very high magnification images.
This microscope is also called the bright-field microscope because the incident light from the source passes through the light source easily to the eye through the two lenses to illuminate the sample specimen clearly.
Parts of a Compound Microscope
There parts of this type microscope is divided into the following two portions:
Non-optical parts of this microscope include the base, pillar, arm, inclination joint, stage, body tube, draw tube, rack and pinion, adjustment screws, and automatic stop.
The optical part of this instrument includes a diaphragm, condenser, reflector, objective lens, oil immersion, and ocular lens.
The non-optical parts description is given below:
Base: This part is also called the foot which is U or horseshoe-shaped. This part is generally constructed of metal which supports the entire microscope.
Pillar: This part helps to create a good connection between the base and the arm.
Arm: This part is generally known as the limb which has a metallic handle. It creates a good connection between the arms to the inclined joint. This part is essential to provide good support between the stage and body.
Inclination Joint: This part helps to keep this instrument in a vertical position during analyses in a sitting position.
Stage: This part is made of metal which is fitted to the lower part of the arm with a hole in the center. The slides of this instrument can be placed easily on the stage either by using side clips or mechanical stage clips.
Body Tube: It holds the sample specimen and ocular lenses at the two ends.
Draw Tube: This tube holds the ocular lenses which are located at the upper end of the body tube.
Rack and Pinion: This part helps to bring the sample specimen under focus. They are generally attached to the body tube or the stage.
Adjustment Screws: These are used for a coarse adjustment or for fine adjustment purposes.
The stage of this instrument moves extremely short distances at the time of fine adjustment is set up. The stage of this instrument moves up at the time of coarse adjustment is set up. A nice image is produced after setting up the fine adjustment.
Automatic Stop: A small screw in the rack and part helps to stop the downward sliding of the body tube. This phenomenon helps to reduce the damage condition of the objective lens.
Optical Parts
Diaphragm: This part helps to control the light falling on the object through the diaphragm. There are two types of diaphragm namely disc and iris.
Condenser: This part is located below the diaphragm which has the ability to focus the light by moving it either up or down position.
Reflector: It is a mirror-type part that is located above the base. This mirror has a plane side on the one side and the other side has a concave mirror. The plane mirror side is used for the strong light and the concave mirror side is used for the weak light. The light of the object can be directed easily with the help of this part through the diaphragm and condenser.
Objective Lenses: These are located over the nose piece which can be lower power, higher power, and oil immersion state.
Ocular Lens: These are generally known as the eyepiece which is used to view the specimen object clearly. There are four types of magnifications are used in this eyepiece which are 5X, 10X, 15X, and 20X.
Advantages of Using Compound Microscope
It is simple to use to get a perfect result. A compound microscope is easy to use and portable. It can be stored easily. A great amount of surface characteristics can be identified by this advanced tool. A lot of information can be collected from the specimen objects for the existence of multiple lenses in this microscope. This microscope has its own light source facility to illuminate sample specimens.
Disadvantages of Compound Microscope
This microscope has a limited magnification facility. As a result, the sample cannot be viewed clearly while the limit of this microscope is crossed.
Applications of Compound Microscope
The presence of metallic substances in minerals can be identified easily by using this tool. This microscope is an essential tool in pathology labs for detecting various harmful microorganisms. It is used in forensic laboratories for detecting various crime samples and is solved by drawing out human cells clearly.
This microscope is used very much in schools, colleges, and universities for conducting various academic experiments. The plant cells as well as various microorganism cells can be analyzed easily through this versatile device. The human fingerprints can be detected by using this tool.
Precautions for Using a Compound Microscope
It must avoid shaking or tilting this microscope at the time of use. The specimen object should be focused with a low-resolution lens before being targeted with a high-resolution lens. It must use the oil to get the perfect result during the use of an oil immersion lens. It should use a clean slide or clean the slide with suitable water before using it.
References
Bardell, D. (2004). The invention of the microscope. Bios, 75(2), 78-84.
Shukla, R. K., Biswas, P., & Yadav, R. S. (2022). Forensic Applications of Compound Microscope. Forensic Microscopy: Truth Under the Lenses.
Genung, E. F. (1942). The development of the compound microscope. Bulletin of the History of Medicine, 12(4), 575-594.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
What is a compound microscope?
It is a crucial tool consisting of two lenses for showing the magnified 2D image of the objective.
What are the uses of a compound microscope?
This microscope is used in the field of academic research, forensic laboratories, diagnostics labs, and various analysis purposes.
What are the parts of a compound microscope?
This microscope has non-optical and optical parts. The non-optical part contains the base, pillar, stage, body tube, draw tube, arm, inclination joint, rack and pinion, adjustment screws, and automatic stop. The optical part contains diaphragm, reflector, objective lens, condenser, oil immersion, and ocular lens.
What are the functions of a compound microscope?
This tool is used very much to view the tiny objects clearly with the naked eye after light passes through the sample.
Who invented the compound microscope?
This microscope was invented by Hans Janssen with Zacharias Janssen back in the year 1590s.

