Matter is any substance that has a specific mass and takes up space. It needs a minimum of one subatomic particle, although most matter consists of atoms. The particles of matter attach to each other in a certain space between them and move continuously. For example, electrons, protons, and neutrons are the most important particles which form atoms.
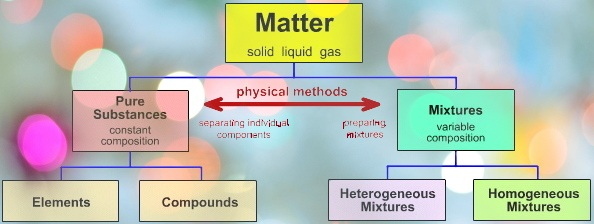
Matter can form different physical states like solid, liquid, gas, and plasma state. The bonding characteristics between atoms reveal the states of matter. The matter can change from one state to another by changing some factors like temperature, pressure, etc. For example, water converts into ice when temperature is decreased. If the temperature is increased, water converts into a vapor state.
Definition of Matter
Matter is any substance having mass and volume. It occupies space and can be weighed. Matter includes atoms, molecules, tiny particles, and any substance that these particles make up. By following the law of conservation of mass, matter can be converted from one to another form through physical and chemical changes. There exist various types of matter like solid, liquid, gases, plasma, Bose-Einstein Condensate State, Superconductive Material State, Color Glass Condensate State, and Time Crystal State.
Classifications of Matter
The matter is mainly classified into pure substances and mixture. There is a good constant composition in pure substance. The specimen from all substances contains the same makeup and properties. For example, the pure sources of sucrose always contain 42.1% carbon, 6.5% hydrogen, and 51.4% oxygen by mass. The sucrose samples from pure sources have the same physical properties like color, sweetness, melting point, etc.
Types of Matter
There are two classes of pure substances namely elements and compounds.
Elements: Elements can be defined as a species of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nucleus. Although an element sometimes contains the same number of protons but has different numbers of masses called isotopes.
Although an element’s atoms have the same number of protons, they can have different numbers of neutrons and hence different masses.
Every element is represented by a specific symbol approved by IUPAC. For example, Nitrogen is represented by N, Oxygen is represented by O, Carbon is represented by C, etc.
The Elements cannot be broken easily into simpler fragments by non-nuclear reactions and can exist as atoms or as molecules. For example, silver, gold, uranium, radium, sodium, and potassium are common elements in our earth. About 90 elements are found in nature and two dozen or so have been created in laboratories by various processes synthetically.
Types of Elements
The elements are kept in a periodic table in a specific way and are divided into their groups as either metallic or non-metallic. Metallic elements are classified into Main Group Metals, Transition Metals, and f-block metals.
Examples of Elements
Elements are found in nature mostly and cannot be broken down further. The elements exist in several forms ions, atoms, isotopes, and molecules. Elements examples are Oxygen atom (O), Oxygen gas (O2), Oxygen ion (O2-) and oxygen isotopes are Oxygen-16, Oxygen-17, and Oxygen-18.
Compounds: Compounds consist of two or more elements that are chemically bound together in a fixed ratio. Compounds can be broken down into elements or various compounds by chemical changes. It can break the crystal of sodium chloride into sodium and chlorine by a chemical process. The sucrose molecule can be broken into the element carbon and the compound water after applying heat in the absence of air. The white solid crystalline silver chloride compound can be broken into silver and chlorine, by absorption of light.
Compounds are generally represented by their specific chemical formula. Actually, it is the way of symbolic representation of a particular chemical compound. We know the atoms in compounds are easily represented by chemical formulas. For example, the chemical formula of potassium chloride is KCl. From this formula, we understand that potassium chloride contains one atom of potassium combined with one atom of chlorine.
Types of compounds
There are two types of compounds namely molecular compounds and salts. The various types of atoms are attached to each other through covalent bonds in molecular compounds. There exist ionic bonds among atoms in salts. Every compound is made by these two types of bonds.
Chemical Mixtures
A mixture is a compound consisting of two or more different chemical components that are not chemically linked. A chemical mixture is also known as a physical blend of two or more chemical substances in which the identities of the individual substances are well preserved. Two or more chemical substances have the form of solutions, suspensions, or colloids.
Types of Mixtures
There are two types of mixtures namely homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. When the composition of a mixture varies from point to point is called a heterogeneous mixture. Two or more chemical components are attached to each other to form a heterogeneous mixture. The heterogeneous components can be distinguished visually and separated easily by physical means. Example: mixture of sand and salt, mixtures of sand and glass particles, water and oil, etc.
When two or more chemical components are attached to each other in a proper way that the various chemical components cannot be visually distinguished, then the resultant mixture is known as a homogeneous mixture. Example: Milk. It is very difficult to separate the components of a homogeneous mixture from a heterogeneous mixture.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a compound?
A compound is a chemical substance usually formed by the different chemical bonding in two or more chemical elements. Example: Water (H2O), Sodium chloride (NaCl), etc.
What are the bonds that lie in chemical compounds?
There are two types of bonds that exist in chemical compounds namely covalent bonds and ionic bonds.
What is the example of the compound?
A compound consists of two or more components in a specific way. Examples: Carbon dioxide (C02), Table salt (NaCl), etc.
What are the types of compounds?
There exist mainly two types of compounds namely molecular compounds and salt compounds. Covalent bonds are found in molecular compounds but salts contain ionic bonds.
What does element mean?
An element consists of atoms with the same atomic number. It is not possible to break the elements into simpler fragments by non-nuclear reactions and can exist as atoms or as molecules.
What are the types of elements?
The elements exist in several forms ions, atoms, isotopes, and molecules. Elements examples are the Hydrogen atom (H), hydrogen gas (H2), and Hydrogen ion (H+) and hydrogen isotopes are hydrogen, deuterium, and tritium.
What is a mixture in chemistry?
A mixture is a chemical compound formed by the combination of two or more different chemical components that are not chemically linked.
What are the types of mixtures?
There exist mainly two types of mixture namely homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
What is a homogeneous mixture?
A homogeneous mixture is a form of mixture in which two or more chemical components are mixed together in such a way that the various chemical components cannot be visually distinguished. Example: Solution of salt in water.
What is a heterogeneous mixture?
A heterogeneous mixture is a form of mixture in which two or more chemical components are mixed together in such a way that the various chemical components can be separated easily. Example: mixture of gold and silver.

