Preparation of standard solution of oxalic acid is essential during standardization to determine the unknown concentration of the secondary standard solution. A standard solution of oxalic acid can be prepared by mixing a specific amount of oxalic acid with distilled water in a volumetric flask.
Theory of the preparation of standard solution of oxalic acid
A standard solution is a crucial solution whose concentration is definitely known and prepared from a primary standard substance like oxalic acid. It is a common primary standard substance that is available in a pure state and is water-soluble in nature. Oxalic acid is less hygroscopic in nature and a stable crystalline substance. The molar mass of oxalic acid is 126 g mol-1. The standard oxalic acid solution can be prepared by weighing a mass of oxalic acid solid and dissolving it in a known volume of solution in a volumetric flask up to the mark.
Materials required for the preparation of standard oxalic acid solution
There are many apparatus required for preparing a standard solution of oxalic acid which are oxalic acid, funnel, distilled water, beaker, glass rod, measuring flask, wash bottle, weighing tube, chemical balance, watch glass, and weighing balance.
Calculation for the preparation of standard solution of oxalic acid
Molecular weight of C2H2O4.2H2O = [{ (12×2) + (1×2) + (16×4)} + 2× {(1×2) + (16×1)}] =126 gm/mol.
Asked concentration, S= 0.03M
The volume of solution=100 ml
We know, W= (SMV/1000)
= {(0.03× 126 × 100)/1000} gm
= 0.378 gm
But, if we take more or less than the above-calculated amount of oxalic acid, we must calculate again to get the actual concentration of this standard solution.
Suppose, we take 0.369 gm of oxalic acid instead of the calculated 0.378 gm of sodium carbonate, then we will calculate the by the following method,
Actual concentration= {(Weight taken × Asked concentration)/weight to be taken)}
= {(0.369× 0.03)/0.378}
=0.0292 M
How to prepare a standard solution of oxalic acid?
The procedure for the preparation of standard solution of oxalic acid is given below:
Procedure
At first, take 0.369 gm of oxalic acid with the help of a weighing scale. Add this chemical into a volumetric flask after placing the funnel on the neck of the volumetric flask. A small amount of distilled water should be added to mix well the oxalic acid. Then add distilled water carefully up to the mark and make the final volume of 100 ml of this solution. Finally, we get the standard oxalic acid solution whose concentration is known.
If we use a beaker to prepare a standard oxalic acid solution, mix the oxalic acid chemical well by using a stirrer with a specific volume of distilled water carefully.
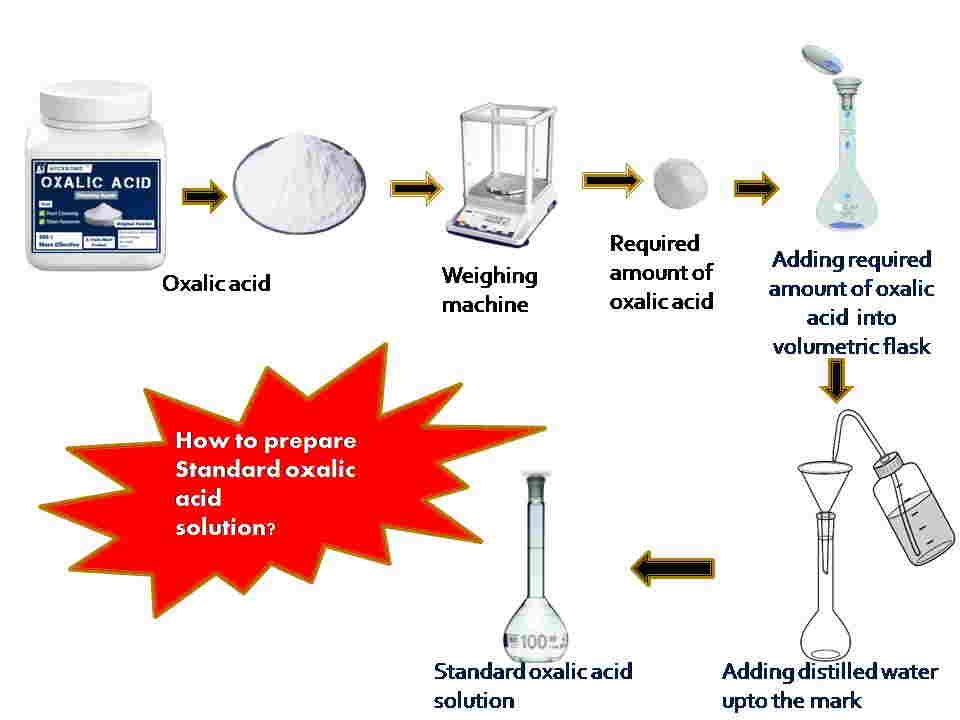
[N.B. = You can prepare different concentrations of standard oxalic acid solution by following the above method]
Precautions for the preparation of standard solution of oxalic acid
It must avoid any spill of the oxalic acid chemical on the balance pan.
The apron must be worn at the time of preparing a standard solution of oxalic acid.
It should handle oxalic acid chemicals carefully because it is corrosive in nature.
The watch glass should be dried for this experiment.
The funnel should be washed thoroughly several times.
It should shake the oxalic acid solution carefully.
Result
The strength of the prepared anhydrous sodium carbonate solution is 0.0292 M.
Important questions for Viva-voce
What is the standard solution in chemistry?
Standard solutions are solutions that have a specific concentration of a substance or element.
What is the standard solution in titration?
Standard solution in titration means the solution (titrant or titrator) containing a precisely known concentration of an element or a substance. A definite amount of solute such as a primary standard is dissolved in a solvent to make a specific volume.
What are the examples of standard solutions?
Standard solution examples are 0.3M Oxalic acid solution, 0.1M oxalic acid solution, 0.2M Sodium carbonate solution, 0.1M HCl solution, 0.2 M H2SO4 solution, etc.
What is the primary standard solution?
A primary standard solution is prepared from a primary standard substance like oxalic acid.
What are the examples of primary standard solutions?
Primary standard solution examples are 0.1M oxalic acid solution, 0.2M oxalic acid solution, 0.3M oxalic acid solution, 0.1M Sodium carbonate solution, etc.
What are the properties of the primary standard solution?
Properties of primary standard solution include a high level of purity, nontoxic, inexpensive, low reactivity, high equivalent weight, and less hygroscopic in nature.
What are the base examples of primary standard chemicals?
Primary standard bases examples are sodium carbonate, potassium hydrogen iodate, potassium dichromate, etc.
Why oxalic acid is a primary standard?
Oxalic acid is a primary standard because it contains a high level of purity, is inexpensive, has low reactivity, has high equivalent weight, and is less hygroscopic in nature.
Why is NaOH not a primary standard?
NaOH is not a primary standard because it is very stable and readily absorbs moisture, and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
What is the formula of oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid formula is C2H2O4 and its usual form is that of the crystalline hydrate whose formula is (COOH)2·2H2O.
What is the molecular weight of oxalic acid?
The molecular weight of oxalic acid is 126 gm/mol.
What is the chemical name of oxalic acid?
The chemical name of oxalic acid is Ethanedioic acid or Oxiric acid.
What is the molecular mass of oxalic acid?
The molecular formula of oxalic acid is C2H2O4 and molecular mass of oxalic acid is 90.03 g/mol. But in most cases, oxalic acid is found in crystalline hydrate whose formula is (COOH)2.2H2O. So, the molecular mass of oxalic acid is 126 g/mol in most cases.
Is oxalic acid molar mass 126 or 90?
Oxalic acid molar mass is 126 because most cases oxalic acid is found in crystalline hydrate.
What is the equivalent weight of oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid equivalent weight is 63 which is calculated by the following:
Equivalent weight of oxalic acid = molecular mass of oxalic acid/2 = 126g/2 = 63 grams.
What is the symbol of oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid symbol is C2H2O4 and most of the cases are (COOH)2·2H2O.
What is the IUPAC name of oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid IUPAC name is Ethanedioic acid.
What happens when oxalic acid and NaOH react with each other?
Oxalic acid and NaOH reactions produce sodium oxalate (Na2C4O4) and water (H2O) molecules.
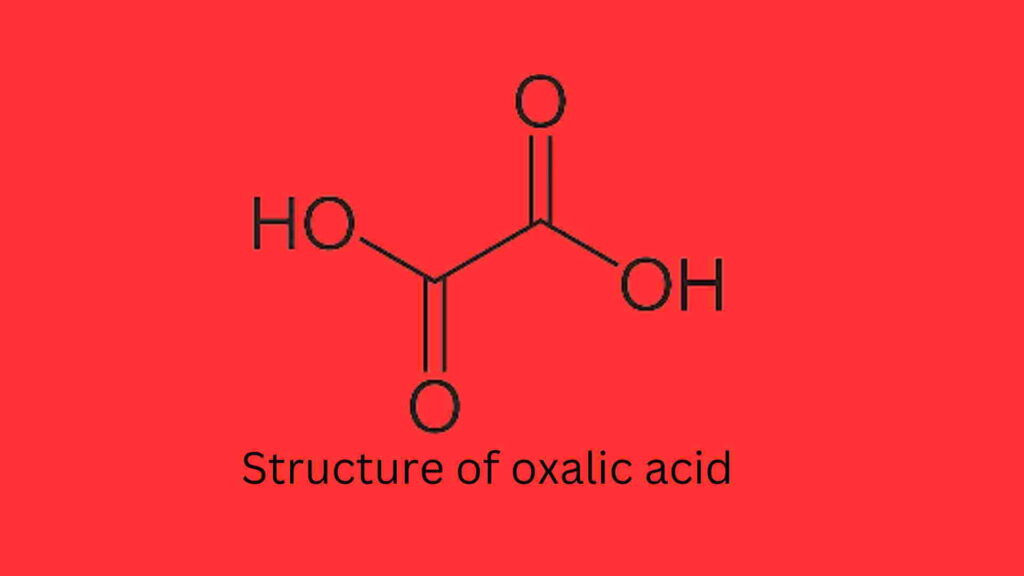
What is the structure of oxalic acid?
The structure of oxalic acid is given below:
What is oxalic acid used for?
Oxalic acid is used to remove rust and various stains from different types of areas like boats, swimming pools, concrete driveways, buildings, iron machinery, wood decks, stairs, or trim. Oxalic acid applications in industries include mineral processing, bleaching clothes, and sterilizing various equipment.
What are the sources of oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid is found in many plants, including leafy greens, fruits, cocoa, nuts, and seeds.
What is the reaction between Oxalic acid and NaOH?
Oxalic acid + NaOH produces sodium oxalate (Na2C4O4) and water (H2O) molecules.
Oxalic acid + NaOH equation is 2NaOH + (COOH)2.2H2O =2COONa + 4H2O
Why oxalic acid is a weak acid?
Oxalic acid consists of two acidic protons and ionizes partially in an aqueous solution. So, it is regarded as a weak acid in nature.
What is the dihydrate formula of oxalic acid?
The oxalic acid dihydrate formula is (COOH)2.2H2O.
What is the melting point of oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid dihydrate melting point ranges from 96 to 1000C.
What is the boiling point of oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid dihydrate boiling point is 149 – 160 °C.
What is the molar mass of oxalic acid dehydrate?
Oxalic acid dihydrate molar mass is 126 g/mol.
What is the pH in oxalic acid solution?
Oxalic acid pH is found in 1.25 to 4.14.
What are the oxalic acid examples?
Oxalic acid examples include kidney stones, cabbage, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts. Oxalic acid can be produced by the metabolism of glyoxylic acid or ascorbic acid in the human body.

