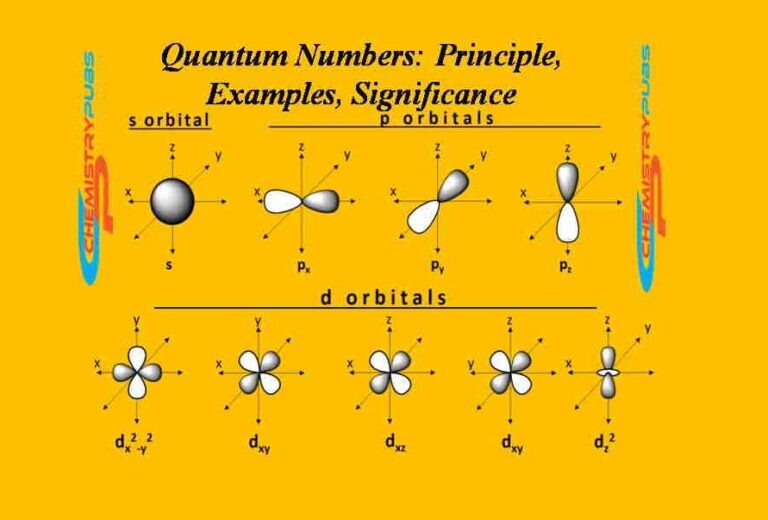
Quantum numbers or electronic quantum numbers represent the electronic trajectory and properties within an atom. Knowing this number is essential to understand the structure of atoms. This set of numbers expresses the location, energy, and direction of an electron within an atom. There exist mainly four types of quantum numbers namely principal, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin quantum numbers.
The energy level within the atom is described by the principal quantum number (n). The azimuthal or angular momentum quantum number (l) expresses the subshell. The orbital of a subshell is represented by – the magnetic quantum number (m). Spin quantum number (s) represents the electronic spin within the atom.
What are Quantum Numbers?
Quantum numbers are a set of numbers to describe the position and energy of an electron within the molecule. The shape, size, and spatial orientation of atomic orbital can be expressed by these numbers. The various properties of orbital are properly understood through this technique.
The four quantum numbers namely principal quantum number, azimuthal quantum number, magnetic quantum number, and spin quantum number to know the information about all of the electrons in an atom. We can know the information about electronic configuration as well as their energy, location, space, and kind of orbital occupied. The direction of orbital within an atom can also be understood by this technique.
There are no two electrons in an atom containing the same set of quantum numbers which was denoted by the Pauli exclusion principle. An integer or half-integer value must be used to characterize each quantum number.
Types of Quantum Numbers
There are four types of quantum numbers that describe the knowledge about the size, shape, orientation of orbitals, and spin of electrons within an atom. The four types of quantum numbers are shown below:
- Principal Quantum Number (n)
- Azimuthal Quantum Number (l)
- Magnetic Quantum Number (ml)
- Electron Spin Quantum Number (s)
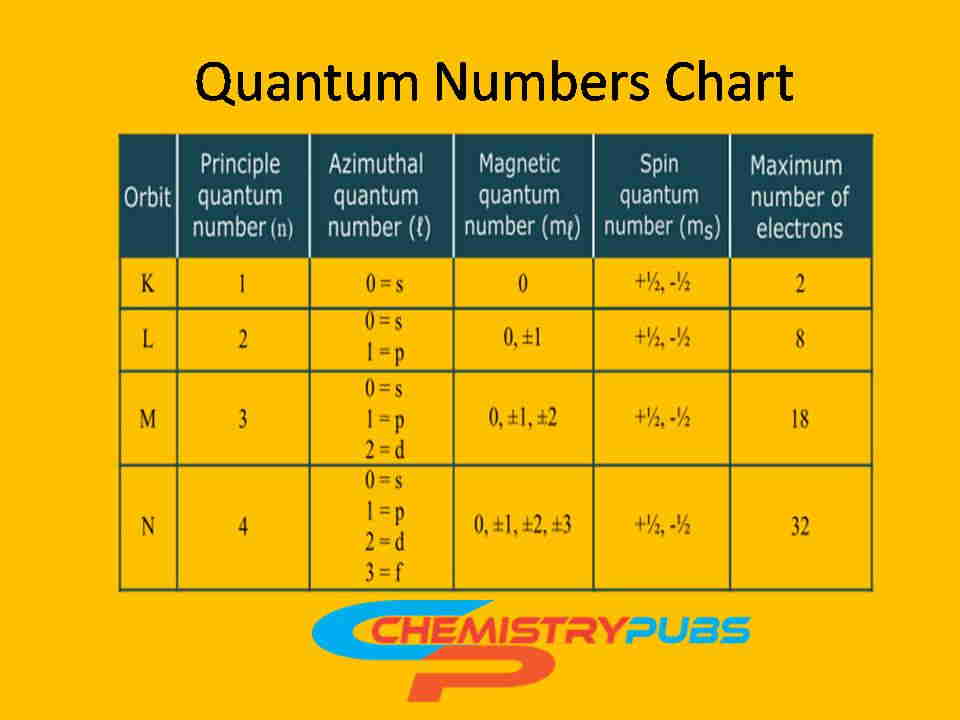
1. Principal Quantum Number (n)
This quantum number relates to expressing the size of the shell of an electron within an atom. The positive integer values of the principal quantum number range from 1 to the shell number of the outermost electrons within an atom by depending on the distance between the electron and the nucleus. The higher number of principal quantum numbers contains more electrons than lower values. This quantum number is essential to express the atomic and ionic radii.
The size of the orbital can be determined easily by this quantum number. The lowest energy level or ground state contains n=1. The electron gains energy and jumps from a lower to a higher energy level then the principal quantum number is increased. When the electron loses energy, it returns to the lower shell and contains the lower value of a principal quantum number.
The size of the orbital is larger when the principal quantum number is high. The principal quantum number does not contain any negative value or zero value because an atom cannot have a negative value or no value for a principal shell. The principal quantum numbers above 4 can also be determined systematically.
The sequence of the various energy shells can be shown as
K < L < M < N < O< P…..
1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5< 6…..
Significance of principal quantum number (n)
It can know the energy and size of the orbit by principal quantum number values.
The level of energy, as well as orbit, increases when increases the value of ‘n’.
The maximum number of electrons in a shell is completely equal to 2n2.
The energy of electrons in hydrogen and hydrogen-like atoms can be determined easily by calculating the principal quantum number values.
The radius of an atom can be determined easily by this number.
The electronic level within an atom is identified by the principal quantum number.
Azimuthal Quantum Number (l)
This quantum number or orbital quantum number relates to the shape of the atomic orbital which is represented by the letter ‘l’. This quantum number calculates the subshell to which an electron belongs. The calculated value of this quantum number equals the total number of angular nodes in the atomic orbital. The value of this quantum number is generally denoted as s, p, d, or f subshell. The value of this quantum number depends on the principal quantum number (n). The value of this quantum number ranges between 0 and (n-1).
For example, if n = 1 (For the 1st Shell, say K), the azimuthal quantum number can have one value: 0
If n = 2 (For the 2nd Shell, say L), the azimuthal quantum number can have two values: 0, and 1
If n = 3 (For the 3rd Shell, say M), the azimuthal quantum number can have three values: 0, 1, and 2
If n = 4 (For the 4th shells), the azimuthal quantum number can have four values: 0, 1, 2, and 3
When l=0 then the resulting subshell is ‘s’ subshell.
When l=1, and 2, the resulting are ‘p’ and ‘d’ subshells respectively.
Now it can be noted that when n=4, the four subshells that can exist are 4s, 4p, 4d, and 4f.
Significance of Azimuthal Quantum Number (l)
The shape of the atomic orbital can be known by calculating the value of azimuthal quantum number.
The total number of angular nodes in the orbital can be identified easily by calculating the value of an azimuthal quantum number.
The energy of the various atomic orbitals can also be calculated by knowing the values of the azimuthal quantum number.
Magnetic Quantum Number (m)
This quantum number relates the orientation of atomic orbital in space which is denoted by the symbol m. The value of this quantum number depends on the Azimuthal quantum number (l). This quantum number has a total number of (2l + 1).
The value of the magnetic quantum number (m) lies between -l and +l. So the values of the magnetic quantum number (m) are indirectly dependent on the value of the principal quantum number (n).
For example,
If n = 1 (For the 1st Shell, say K), the Azimuthal quantum number can have one value (0) which indicates the presence of s subshell. Then the magnetic quantum number contains value 0.
If n = 2 (For the 2nd Shell, say L), the Azimuthal quantum number can have two values (0, and 1) which indicate the presence of s, and p subshell. Then the magnetic quantum number contains three values (-1, 0, and +1).
If n = 3 (For the 3rd Shell, say M), the Azimuthal quantum number can have three values (0, 1, and 2) which indicates the presence of s, p, and d subshell. Then the magnetic quantum number contains five values (-2, -1, 0, +1, and +2).
If n = 4 (For the 4th Shell, say N), the Azimuthal quantum number can have four values (0, 1, 2, and 3) which indicates the presence of s, p, d, and f subshell. Then the magnetic quantum number contains seven values (-3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, and +3).
Significance of Magnetic Quantum Number (m)
The orbital angular momentum can be identified by calculating the magnetic quantum number values.
The number of preferred orientations of the electrons in an atom can be identified by calculating the magnetic quantum number values.
The spatial arrangement of atomic orbital can be identified by calculating the magnetic quantum number values.
The number of various orbital presences can also be identified by calculating the magnetic quantum number values.
Electron Spin Quantum Number (ms)
This quantum number relates to the spinning of electrons in the atom which is by the symbol ms. This quantum number does not depend on the principal quantum number, azimuthal quantum number, and magnetic quantum number.
The value of this quantum number lies between +1/2 and -1/2.
The positive value of this quantum number expresses the upward spin on the electron and the negative value of this quantum number expresses the downward spin on the electron
This value helps to identify the presence of a magnetic field in an atom whose value can be generalized to ±½.
Significance of Electron Spin Quantum Number (ms)
The direction of electron spin is identified by calculating the values of the electron spin quantum number.
The clockwise and anti-clockwise direction spin is identified by calculating the values of the electron spin quantum number.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are Quantum numbers?
Quantum numbers are the values related to the location, energy, and direction of an electron within an atom. The shape of the energy level and spin direction of an electron in an atom can be identified by calculating the values of quantum numbers.
What are the types of quantum numbers?
There exist four types of quantum numbers namely principal quantum number, azimuthal quantum number, magnetic quantum number, and spin quantum number.
What is the principal quantum number?
The principal quantum number describes the electronic orbit or main energy level within an atom which is denoted by n. The higher number of principal quantum numbers contains more electrons than lower values. When n=1, 2, 3, and 4 then this quantum number expresses as K, L, M, and N shell respectively.
What is the azimuthal quantum number?
This quantum number expresses the subshell of the electronic orbit within the molecule. The energy as well as the total number of angular nodes in the orbital can be identified by calculating the values of this quantum number.
What is the magnetic quantum number?
This magnetic quantum number relates the orientation of atomic orbital in space which is denoted by the symbol m.
What is the spin quantum number?
The spin quantum number expresses the spinning direction of electrons in the atom which is denoted by ms.