Titration of Oxalic Acid with KMnO4 associates with the redox reaction. The concentration KMnO4 can be determined by oxalic acid solution.
Theory of the titration of Oxalic Acid with KMnO4
Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) is a strong oxidizing agent and it acts as a powerful oxidizing agent in an acidic medium during the titration of Oxalic Acid with KMnO4 that can be represented by the following equation:
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 + 5(COOH)2 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 8H2O + 10CO2 ↑
The above equation can be written as the following ionic equation:
MnO4– + 8H+ + 5e– → Mn2+ + 4H2O
The MnO4– ions in the acidic solution are purple in color but the solution containing Mn2+ ions are colorless. So, it can be noted that the solution turns colorless during the addition of a reducing agent into a permanganate solution. If there is presence excess of potassium permanganate, the solution will turn purple in color. Hence, Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) serves as a self-indicator in an acidic solution.
Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) can be standardized against pure oxalic acid solution. It is associated with a redox reaction where oxalic acid (COOH-COOH) is oxidized to carbon dioxide by KMnO4, which itself gets reduced to MnSO4.
Chemical reaction
Reduction Half reaction in this titration is given below:
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 3H2O + 5[O]
Oxidation Half reaction in this titration is given below:
5(COOH)2 + 5[O] → 5H2O + 10CO2 ↑
The overall reaction in this titration is given below:
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 + 5(COOH)2 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 8H2O + 10CO2 ↑
The ionic equation during the titration of Oxalic Acid with KMnO4
Reduction Half reaction in this titration is given below:
[MnO4– + 8H+ + 5e– → Mn2+ + 4H2O] x 2
Oxidation Half reaction in this titration is given below:
[C2O42- → 2CO2 + 2e–] x 5
The overall Ionic reaction in this titration is given below:
2MnO4– + 16H+ + 5C2O42– → 2Mn2+ + 10CO2 + 8H2O
Material required for the titration of Oxalic Acid with KMnO4
Burette, pipette, measuring flask, conical flask, funnel, weighing bottle, chemical balance, oxalic acid, potassium permanganate solution, 1.0 M sulphuric acid.
Apparatus setup for the titration of Oxalic Acid with KMnO4
KMnO4 solution should be taken in the burette and oxalic acid (COOH-COOH) solution should be taken in a conical flask.
Procedure for the titration of Oxalic Acid with KMnO4
Step-1: Preparation of 0.1M standard solution of oxalic acid (COOH-COOH)
At first, we must calculate the amount required for 0.1 M of oxalic acid. We know that the molecular weight of oxalic acid is 126 gm. So, we require 1.26 g oxalic acid per 100 ml of solution. It needs to be weighed carefully in an electric balance to measure the amount of oxalic acid dehydrated. Then prepare 100ml of 0.1M oxalic acid solution in a volumetric flask up to the marked point with distilled water.
Step-2: Titration of KMnO4 against standard oxalic acid solution
At first, fill the burette with KMnO4 solution. Then take out 10ml of 0.1M standard oxalic acid solution into a conical flask. Add a few drops of H2SO4 in order to prevent oxidation of manganese to form manganese dioxide.
Then heat the mixture up to 60 degrees Celsius before titrating it with KMnO4 solution. It should note down the initial burette reading before starting the titration. Then, the hot solution should be titrated against potassium permanganate (KMnO4) solution while gently swirling the solution in the flask. It will be found that the purple color of the potassium permanganate (KMnO4) solution is discharged with oxalic acid (COOH-COOH). Finally, it will be seen that a permanent pink color signal indicates the end point of this titration.
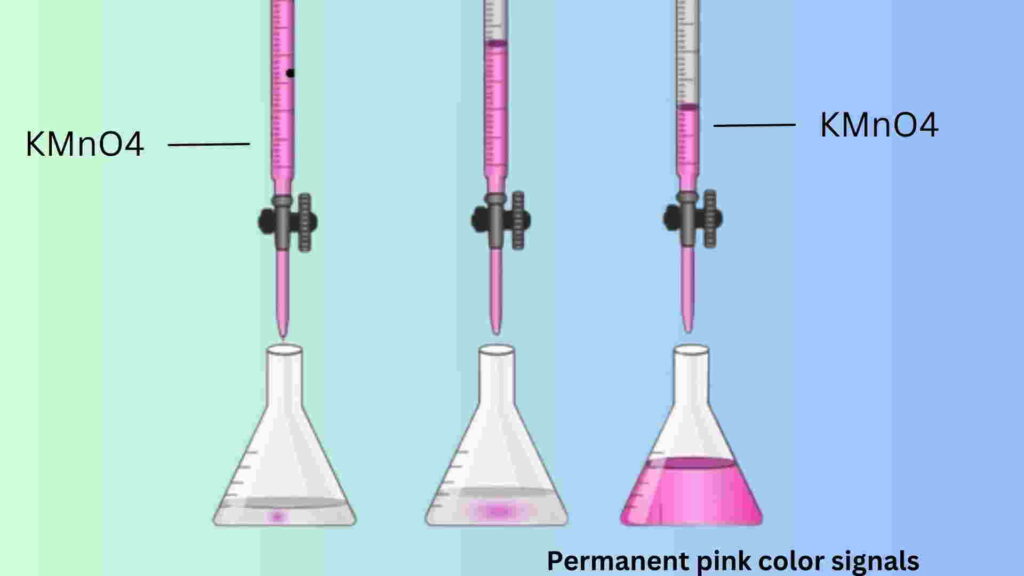
Repeat this titration at least 3 times and note down the upper meniscus on the burette readings to input this data in the observation table and for calculation.
Table for the standardization of KMnO4 with oxalic acid
The table for the standardization of KMnO4 with oxalic acid is given here. It can be noted that the following values can be changed based on your experiment.
| Number of observation | Amount of oxalic acid taken (ml) | Initial burette reading (ml) | Final burette reading (ml) | Amount of KMnO4 consumed (ml) | Average volume of KMnO4 consumed (ml) |
| 1 | 10 | 40 | 26 | 14 | |
| 2 | 10 | 26 | 11.8 | 14.2 | 14.167 |
| 3 | 10 | 40 | 25.7 | 14.3 |
Standardization of KMnO4 with oxalic acid calculation
We get the following information from the balanced chemical reaction during the titration of Oxalic Acid with KMnO4
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 + 5(COOH)2 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 8H2O + 10CO2 ↑
From the above reaction, 5-mole oxalic acid= 2 mole KMnO4
We can apply the following formula to get the strength of the potassium permanganate solution:
5 Moxalic acid x Voxalic acid = 2 MKMnO4 x VKMnO4
or, M KMnO4 = (5 Moxalic acid x Voxalic acid)/ VKMnO4
= (5 x 0.1 x 10)/14.167
= 0.3529 M
Result: The strength of KMnO4 is 0.3529 M.
Precautions during the titration of Oxalic Acid with KMnO4
It must clean all the apparatus with distilled water and then rinse with the solution to be taken in them before starting this experiment.
It must rinse the pipette properly before starting this experiment.
It should use dilute sulfuric acid for acidifying the KMnO4.
It should carefully read the upper meniscus because the KMnO4 solution is dark in color.
It should take out the accurate readings once it reaches the endpoint.
It must avoid the rubber cork burette as it can be attacked by KMnO4.
Important viva question related to the titration of Oxalic Acid with KMnO4
What is standardization in chemistry?
Standardization in chemistry relates to the process of determining the specific strength of a solution.
What is the importance of standardization in chemistry?
Standardization in chemistry helps to determine the purity and strength of taken solution.
What is titration?
Titration in chemistry is a type of analysis technique that is used to calculate the concentration of a given analyte in a mixture.
What are the types of titration?
Titration is divided into three categories namely acid-base titration, redox titration, and Iodometry Titration.
What is titrant?
The titrant is typically a strong acid or base that is added to the titrand in a titration experiment. The concentration of this solution is known and is usually added to the titrand using a burette.
What is titrand?
The titrand is a type of solution whose concentration is unknown and is determined through the use of the titrant. This solution is usually an acid or base that can be neutralized by the titrant.
What is the standard solution in titration?
Standard solution in titration means the solution that contains a specific known concentration of an element or a substance.
What are the examples of standard solutions?
Standard solution examples are 0.4M Oxalic acid solution, 0.2M oxalic acid solution, 0.3M Sodium carbonate solution, 0.2M HCl solution, 0.3 M H2SO4 solution, etc.
What is the primary standard solution?
A primary standard solution is a solution that is prepared from a primary standard substance.
What are the examples of primary standard solutions?
Primary standard solution examples are 0.2M oxalic acid solution, 0.1M oxalic acid solution, 0.4M oxalic acid solution, 0.2M Sodium carbonate solution, etc.
What are the properties of the primary standard solution?
Properties of the primary standard solution include a good level of purity, nontoxic, cheap, low reactivity, higher equivalent weight, and lower hygroscopic in nature.
Why oxalic acid is a primary standard?
Oxalic acid is a primary standard because it contains a good level of purity, is non-toxic, is cheap, has low reactivity, higher equivalent weight, and is lower hygroscopic in nature.
What is the formula of oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid’s general formula is C2H2O4 and its usual form is that of the crystalline hydrate (COOH)2·2H2O.
What is the molecular weight of oxalic acid?
The molecular weight of oxalic acid is 126 gm/mol because its usual form is that of the crystalline hydrate (COOH)2·2H2O.
What is the molecular mass of oxalic acid?
The molecular mass of oxalic acid is 126 gm/mol due to the existence of crystalline hydrate whose formula is (COOH)2·2H2O in most of the cases.
Is oxalic acid molar mass 126 or 90?
Oxalic acid’s molar mass is 126 because its usual form is that of the crystalline hydrate (COOH)2·2H2O.
What is the equivalent weight of oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid equivalent weight is 63 which can be shown that the molecular mass of oxalic acid/2 = 126g/2 = 63 grams.
What is the symbol of oxalic acid?
The oxalic acid symbol is C2H2O4 and its usual form is that of the crystalline hydrate (COOH)2·2H2O.
What is the formula of potassium permanganate?
The formula of potassium permanganate is KMnO4.
What is the molar mass of KMnO4?
The molar mass of KMnO4 is 158.034 g/mol.
What are the uses of KMnO4?
KMnO4 is widely used in various chemical industries and laboratories as a strong oxidizing agent.
What is redox titration?
Redox titration in chemistry is a type of titration that determines the titrand or analyte concentration by carrying out a redox reaction between the analyte and the titrant after adding a redox indicator or a potentiometer.
What is redox reaction?
A redox reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred between two reactants participating in it. This transfer of electrons in this reaction can be identified by observing the changes in the oxidation states of the reacting species.
What is oxidation?
Oxidation is defined as the process in which an atom or ion loses one or more electrons during a reaction.
What is Reduction?
Reduction is a process in which an atom or ion gains one or more electrons during a reaction.
What is the endpoint?
The endpoint in chemistry defines a change in color or intensity and indicates that the chemical process has reached its conclusion.

