An atom consists of the smallest particle of matter referred to as subatomic particles protons, neutrons, and electrons. The subatomic particles combine in different proportions to form atoms. These are available mostly as the form of ions and molecules to form matter that we see, feel, and touch. All the things in the known universe are formed by these tiny particles. These are responsible for the formation of various chemical reactions in nature.
Atom Definition
It is defined as the proper combination of subatomic particles to participate in a chemical reaction. The building block of all matter in our universe is formed by atoms. They are the basic items for all types of materials. There exist 118 known elements in the Periodic Table. Among these, 92 of them occur naturally, and other atoms were invented in the laboratory. These determine the elemental characteristics to show the various chemical reactions in nature.
They are able to interact with each other through bonding to the formation of various complex molecules. The interaction characteristics determine the formation of various states of matter like solids, liquids, or gases.
The structure of an atom
It is the smallest part of any type of element. It contains a nucleus, proton, neutron, and outer shell electrons. The introduction to these parts is discussed below:
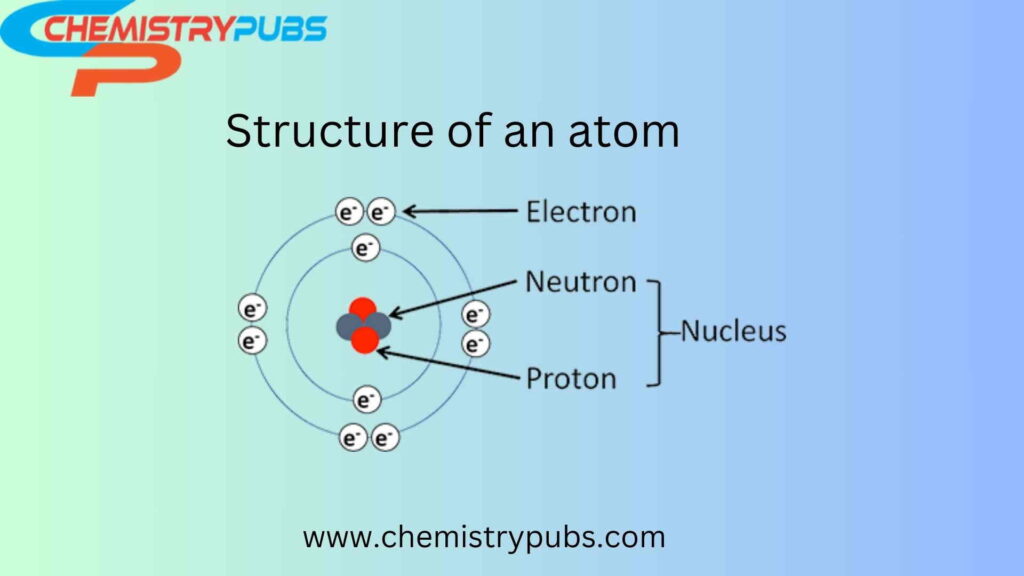
Electrons
These are negatively charged particles that remain in the outermost shell of an atom surrounding the nucleus. It was discovered by. J. Thomson in 1897 after conducting a cathode ray tube experiment. The charge of electron and proton is completely equal and opposite held by the atom. So, atoms have neutral characteristics in nature.
Properties of Electrons
An electron has a negative charge unit which is -1.602 ×10-19 Coulombs.
The invariant mass of an electron is very small which is 9.1093 ×10-31 Kg.
The mass of an electron is 1/1837 times less than the mass of a proton.
The mass of an electron is 1/2000 times lesser than the mass of a proton and neutron
These are found outside the nucleus like protons.
These subatomic particles move continuously around the nucleus in orbits or shells.
Electrons contain both particle and wave properties.
It is not possible to determine the position and momentum of the electrons simultaneously.
Protons
These are positively charged sub-atomic particles invented by Goldstein in 1886. The number of protons determines the position of an atom in the periodic table.
Properties of protons
Protons consist of a positive charge which is +1.602 × 10-19 Coulombs.
The charge of this particle is equal to the number of charges in an electron.
The charge of this particle is +1.602 × 10-19 Coulombs.
The mass of a proton is 1.676 × 10 -27 Kg which is negligible and equal to a hydrogen atom mass.
Three quarks are made to this particle where two up quarks and one down quark are held together by gluons.
Neutrons
These are subatomic particles and have no charges. The mass of this particle is slightly greater than a proton in magnitude. The concept of this subatomic particle was introduced by Ernest Rutherford in 1920 and it was discovered by the British physicist James Chadwick in 1932.
Properties of Neutrons
There is no charge of this subatomic particle.
The mass of this particle is 1.676 × 10-27 Kg.
This particle is greatly affected by the presence of the magnetic field.
The electric fields do not create any effect on this subatomic particle.
History of Atom
According to Stephen Hawking’s Big Bang Theory, atoms were created in 13.7 billion years ago. But Electrons and quarks were created millions of years later as the universe cools down then quarks were aggregated to form protons and neutrons which on further engagement created atoms. These atoms combine to form all the matter in the universe. Indian philosophers thought about the properties of matter a thousand years ago. They suggested that matter is created by smaller particles called “Anu” and “Parmanu”. The modern concept of the atom was first given by John Dalton in 1803.
Size of an Atom
It is defined as the how much distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost shell of an atom and expressed in terms of its radius. An atom is a very tiny particle and cannot be seen through the naked eye. It can be seen by a very powerful electron microscope. However, it is very difficult to calculate the actual size of an atom as well as the electron location with respect to the nucleus. However, it can be estimated the radius of an atom is 10-9 m. The atomic size of hydrogen is 10-10 m.
Atomic Mass
It is defined as the total number of protons and neutrons in an element. This relative concept is generally measured by amu (Atomic Mass Units). 1 amu is equivalent to the 1/12 mass of the carbon (C-12) atom. The sum of the number of protons and neutrons is called the atomic mass of the element. The atomic mass as the name suggests is the mass of the atoms. As we know atoms are made up of electrons, protons, and neutrons and the mass of protons and neutrons is exponentially higher than the mass of electrons so to find the mass of the atom we find the number of protons and neutrons in the atom. Hence if we say that the mass of a magnesium atom is 24 amu, it means that it is 24 times heavier than 1/12 of the C-12 atom.
Atomic Number
It is the number of protons in an element that is used to differentiate one element from another. It expresses the various characteristics of an atom.
Atomic Number of Elements
The atomic numbers of elements with their symbol are discussed below:
The atomic number of Hydrogen is 1 and the symbol of Hydrogen is H.
The atomic number of Helium is 2 and the symbol of Helium is He.
The atomic number of Lithium is 3 and the symbol of Lithium is Li.
The atomic number of Beryllium is 4 and the symbol of Beryllium is Be.
The atomic number of Boron is 5 and the symbol of Boron is B.
The atomic number of Carbon is 6 and the symbol of Carbon is C.
The atomic number of Nitrogen is 7 and the symbol of Nitrogen is N.
The atomic number of Oxygen is 8 and the symbol of Oxygen is O.
The atomic number of Fluorine is 9 and the symbol of Fluorine is F.
The atomic number of Neon is 10 and the symbol of Neon is Ne.
The atomic number of Sodium is 11 and the symbol of Sodium is Na.
The atomic number of Magnesium is 12 and the symbol of Magnesium is Mg.
The atomic number of Aluminum is 13 and the symbol of Aluminum is Al.
The atomic number of Silicone is 14 and the symbol of Silicone isSi.
The atomic number of Phosphorus is 15 and the symbol of Phosphorus isP.
The atomic number of Sulphur is 16 and the symbol of Sulphur is S.
The atomic number of Chlorine is 17 and the symbol of Chlorine is Cl.
The atomic number of Argon is 18 and the symbol of Argon is Ar.
The atomic number of Potassium is 19 and the symbol of Potassium is K.
The atomic number of Calcium is 20 and the symbol of Calcium is Ca.
The atomic number of Scandium is 21 and the symbol of Scandium is Sc.
The atomic number of Vanadium is 22 and the symbol of Vanadium is V.
The atomic number of Titanium is 23 and the symbol of Titanium is Ti.
The atomic number of Chromium is 24 and the symbol of Chromium is Cr.
The atomic number of Manganese is 25 and the symbol of Manganese is Mn.
The atomic number of Iron is 26 and the symbol of Iron is Fe
The atomic number of Cobalt is 27 and the symbol of Cobalt is Co.
The atomic number of Nickel is 28 and the symbol of Nickel is Ni.
The atomic number of Copper is 29 and the symbol of Copper is Cu.
The atomic number of Zinc is 30 and the symbol of Zinc is Zn.
The atomic number of Gallium is 31 and the symbol of Gallium is Ga.
The atomic number of Germanium is 32 and the symbol of Germanium is Ge.
The atomic number of Arsenic is 33 and the symbol of Arsenic is As.
The atomic number of Selenium is 34 and the symbol of Selenium is Se.
The atomic number of Bromine is 35 and the symbol of Bromine is Br.
The atomic number of Krypton is 36 and the symbol of Krypton is Kr.
The atomic number of Rubidium is 37 and the symbol of Rubidium is Rb.
The atomic number of Strontium is 38 and the symbol of Strontium is Sr.
The atomic number of Yttrium is 39 and the symbol of Yttrium is Y.
The atomic number of Zirconium is 40 and the symbol of Zirconium is Zr.
The atomic number of Niobium is 41 and the symbol of Niobium is Nb.
The atomic number of Molybdenum is 42 and the symbol of Molybdenum is Mo.
The atomic number of Technetium is 43 and the symbol of Technetium is Tc.
The atomic number of Ruthenium is 44 and the symbol of Ruthenium is Ru.
The atomic number of Rhodium is 45 and the symbol of Rhodium is Rh.
The atomic number of Palladium is 46 and the symbol of Palladium is Pd.
The atomic number of Silver is 47 and the symbol of Silver is Ag.
The atomic number of Cadmium is 48 and the symbol of Cadmium is Cd.
The atomic number of Indium is 49 and the symbol of Indium is In.
The atomic number of Tin is 50 and the symbol of Tin is Sn.
The atomic number of Antimony is 51 and the symbol of Antimony is Sb.
The atomic number of Tellurium is 52 and the symbol of Tellurium is Te.
The atomic number of Iodine is 53 and the symbol of Iodine is I.
The atomic number of Xenon is 54 and the symbol of Xenon is Xe.
The atomic number of Cesium is 55 and the symbol of Cesium is Cs.
The atomic number of Barium is 56 and the symbol of Barium is Ba.
The atomic number of Lanthanum is 57 and the symbol of Lanthanum is La.
The atomic number of Cerium is 58 and the symbol of Cerium is Ce.
The atomic number of Praseodymium is 59 and the symbol of Praseodymium is Pr.
The atomic number of Neodymium is 60 and the symbol of Neodymium is Nd.
The atomic number of Promethium is 61 and the symbol of Promethium is Pm.
The atomic number of Samarium is 62 and the symbol of Samarium is Sm.
The atomic number of Europium is 63 and the symbol of Europium is Eu.
The atomic number of Gadolinium is 64 and the symbol of Gadolinium is Gd.
The atomic number of Terbium is 65 and the symbol of Terbium is Tb.
The atomic number of Dysprosium is 66 and the symbol of Dysprosium is Dy.
The atomic number of Holmium is 67 and the symbol of Holmium is Ho.
The atomic number of Erbium is 68 and the symbol of Erbium is Er.
The atomic number of Thulium is 69 and the symbol of Thulium is Tm.
The atomic number of Ytterbium is 70 and the symbol of Ytterbium is Yb.
The atomic number of Lutetium is 71 and the symbol of Lutetium is Lu.
The atomic number of Hafnium is 72 and the symbol of Hafnium is Hf.
The atomic number of Tantalum is 73 and the symbol of Tantalum is Ta.
The atomic number of Tungsten is 74 and the symbol of Tungsten is W.
The atomic number of Rhenium is 75 and the symbol of Rhenium is Re.
The atomic number of Osmium is 76 and the symbol of Osmium is Os.
The atomic number of Iridium is 77 and the symbol of Iridium is Re.
The atomic number of Platinum is 78 and the symbol of Platinum is Pt.
The atomic number of Gold is 79 and the symbol of Gold is Re.
The atomic number of Mercury is 80 and the symbol of Mercury is Hg.
The atomic number of Thallium is 81 and the symbol of Thallium is TI.
The atomic number of Lead is 82 and the symbol of Lead is Pb.
The atomic number of Bismuth is 83 and the symbol of Bismuth is Bi.
The atomic number of Polonium is 84 and the symbol of Polonium is Po.
The atomic number of Astatine is 85 and the symbol of Astatine is At.
The atomic number of Radon is 86 and the symbol of Radon is Rn.
The atomic number of Francium is 87 and the symbol of Francium is Fr.
The atomic number of Radium is 88 and the symbol of Radium is Ra.
The atomic number of Actinium is 89 and the symbol of Actinium is Ac.
The atomic number of Thorium is 90 and the symbol of Thorium is Th.
The atomic number of Protactinium is 91 and the symbol of Protactinium is Pa.
The atomic number of Uranium is 92 and the symbol of Uranium is U.
The atomic number of Neptunium is 93 and the symbol of Neptunium is Np.
The atomic number of Plutonium is 94 and the symbol of Plutonium is Pt.
The atomic number of Americium is 95 and the symbol of Americium is Am.
The atomic number of Curium is 96 and the symbol of Curium is Cm.
The atomic number of Berkelium is 97 and the symbol of Berkelium is Bk.
The atomic number of Californium is 98 and the symbol of Californium is Cf.
The atomic number of Einsteinium is 99 and the symbol of Einsteinium is Es.
The atomic number of Fermium is 100 and the symbol of Fermium is Fm.
The atomic number of Mendelevium is 101 and the symbol of Mendelevium is Md.
The atomic number of Nobelium is 102 and the symbol of Nobelium is No.
The atomic number of Lawrencium is 103 and the symbol of Lawrencium is Lr.
The atomic number of Rutherfordium is 104 and the symbol of Rutherfordium is Rf.
The atomic number of Dubnium is 105 and the symbol of Dubnium is Db.
The atomic number of Seaborgium is 106 and the symbol of Seaborgium is Sg.
The atomic number of Bohrium is 107 and the symbol of Bohrium is Bh.
The atomic number of Hassium is 108 and the symbol of Hassium is Hs.
The atomic number of Meitnerium is 109 and the symbol of Meitnerium is Mt.
The atomic number of Darmstadtium is 110 and the symbol of Darmstadtium is Ds.
The atomic number of Roentgeniumis 111 and the symbol of Roentgenium is Rg.
The atomic number of Copernicium is 112 and the symbol of Copernicium is Cn.
The atomic number of Nihonium is 113 and the symbol of Nihonium is Nh.
The atomic number of Fleroviumis 114 and the symbol of Flerovium is Fl.
The atomic number of Moscovium is 115 and the symbol of Moscovium is Mc.
The atomic number of Livermorium is 116 and the symbol of Livermorium is Lv.
The atomic number of Tennessine is 117 and the symbol of Tennessine is Ts.
The atomic number of Oganesson is 118 and the symbol of Oganesson is Og.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an atom?
It is the smallest part of an element which contains protons and neutrons inside the nucleus with negatively charged electrons around the nucleus. Atom has the ability to participate in a chemical reaction and exist independently in nature.
What is the atomic number?
It represents the number of protons in the atom of an element is called the atomic number of the element. The symbol of atomic number is Z. For example: the atomic number of magnesium is 12 which means that Magnesium contains 12 protons in the nucleus of its atom.
What is mass number?
It represents the total number of protons and neutrons present in an element. For example, Magnesium contains mass number 24 which expresses that it contains the protons and neutrons number 24.
What are the differences between atomic number and mass number?
Atomic number represents the number of protons present in an atom, whereas mass number represents the number of protons and neutrons present in an atom. The atomic number contains a smaller value than a mass number.
What is a proton?
It is a positively charged subatomic particle that remains in an atomic nucleus with neutrons. This elementary particle helps to show various characteristics of an atom.
What is an electron?
It is a negatively charged subatomic particle that remains around the nucleus. This elementary subatomic particle exists always outside of the nucleus.
What is a neutron?
It stays in the nucleus and contains no charge of its own. It is the necessary constituent of any atomic nucleus.
What is the nucleus in chemistry?
It is a positively charged part of an atom that stays at the center of the atom. The subatomic particle protons and neutrons stay in the nucleus. The protons in the nucleus have a positive charge, whereas neutrons have no charge of their own.
What is a molecule?
It is a group of atoms where two or more two atoms of the same or different elements are chemically bonded together. For example, two atoms of oxygen and one atom of carbon react to form one molecule of carbon dioxide molecule.
What are the differences between atoms and molecules for example?
An atom is the fundamental part of an element, whereas a molecule contains two or more atoms. An atom shows less stability than a molecule. For example, Sodium (Na) is an atom whereas Sodium Chloride (NaCl) is a molecule.
What is the definition of an atom?
An atom is the smallest part of matter and consists of a single nucleus with one or more number of protons, electrons, and neutrons. The nucleus of an atom contains a positive charge, whereas electrons show a negative charge.
What are the differences between elements and atoms?
An atom is the smallest part of an element, whereas an element is the simplest form of a substance. Atoms consist of electrons, protons, and neutrons whereas an element contains only one type of atom. Atoms are lighter than elements. There exist 92 different kinds of atoms in nature, whereas the total number of elements is 118.

